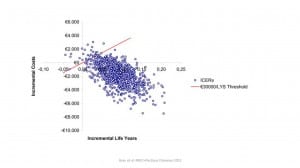
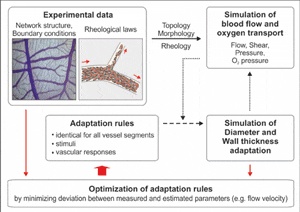
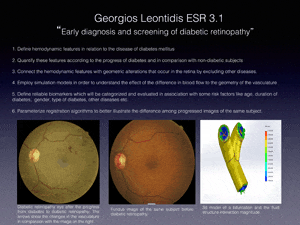
 The beginning of this reporting period was mostly devoted to researching background information for my REVAMMAD project. Along with the literature review, my first step in the practical research included the creation of a data structure based on the object oriented programming technique.
The beginning of this reporting period was mostly devoted to researching background information for my REVAMMAD project. Along with the literature review, my first step in the practical research included the creation of a data structure based on the object oriented programming technique.
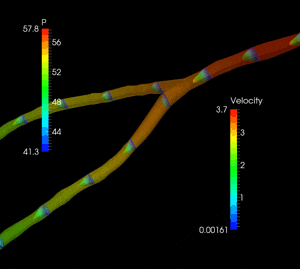
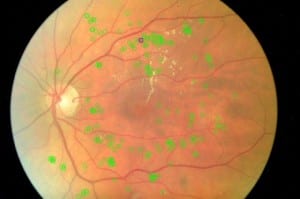
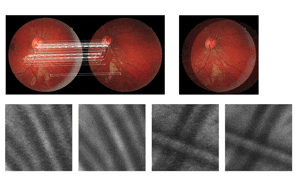
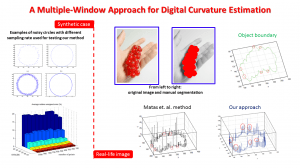
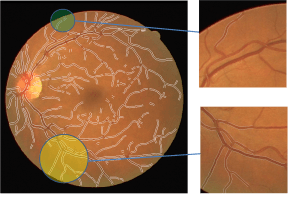
Recently I started to create a new algorithm which at the first stage it is able to group the vascular segments present within a certain region, and in the future this algorithm will be able to connect these segments automatically.