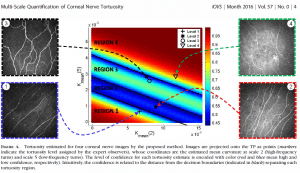
 Type 2 diabetes represents the most prevalent cause for progression of diabetic retinopathy. However, there is a lack of appropriate translation animal models. Although the renin-angiotensin system plays an important role in the progression of diabetic retinopathy, its influence in diabetic retinopathy has not been systematically evaluated. Here we test the suitability of a new model, the TetO rat, addressing the role of angiotensin-II receptor 1 (AT1) blockade in experimental diabetic retinopathy.
Type 2 diabetes represents the most prevalent cause for progression of diabetic retinopathy. However, there is a lack of appropriate translation animal models. Although the renin-angiotensin system plays an important role in the progression of diabetic retinopathy, its influence in diabetic retinopathy has not been systematically evaluated. Here we test the suitability of a new model, the TetO rat, addressing the role of angiotensin-II receptor 1 (AT1) blockade in experimental diabetic retinopathy.
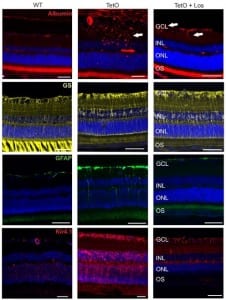
Diabetes was induced by tetracycline-inducible small hairpin RNA (shRNA) knock-down of the insulin receptor in rats (TetO). Systemic treatment consisted of an AT1-antagonist (ARB) at the onset of diabetes. 4-5 weeks later, the retina was analyzed in vivo and ex vivo. Retinal function was assessed by Ganzfeld ERG.
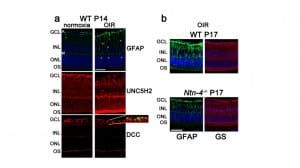
Retinal vessels in TetO showed calibre differences together with gliosis. The total number as well as the proportion of activated mononuclear phagocytes was increased. TetO presented loss of retinal ganglion cells (RGC). ERG indicated photoreceptor malfunction. Both the inner and outer blood-retina-barrier were affected.
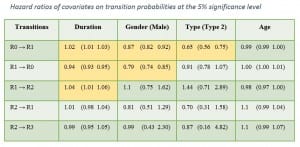
The ARB-treated group presented reduced gliosis and an overall amelioration of the retinal function together with RGC recovery. No statistically significant effects on vascular and inflammatory features were found.
TetO rat represents a promising translational model for early neurovascular changes of type 2 diabetic retinopathy. ARB treatment revealed an effect on the neuronal component but not on the vasculature.
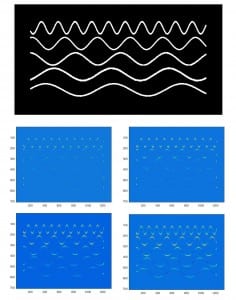
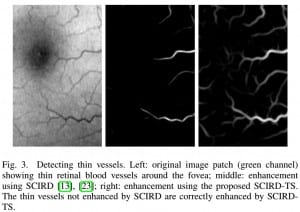
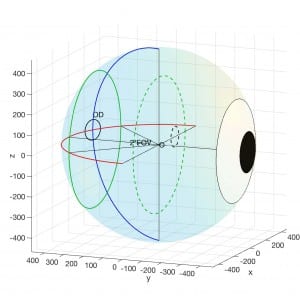
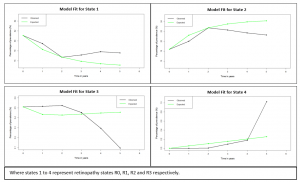
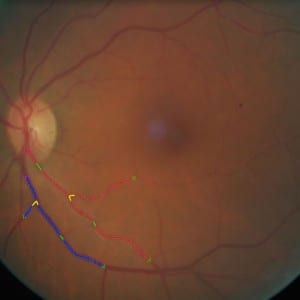 with Georgios, a longitudinal study of twenty-four subjects was conducted. In this study, we monitored the retinal haemodynamics during the three years before the appearance of diabetic retinopathy (DR) and in the first year of DR. We took vascular measurements from standard fundus images, and estimated fluidynamic parameters using a simple haemodynamic model. We show that there are statistically significant changes in some estimated haemodynamic parameters associated with the development of DR.
with Georgios, a longitudinal study of twenty-four subjects was conducted. In this study, we monitored the retinal haemodynamics during the three years before the appearance of diabetic retinopathy (DR) and in the first year of DR. We took vascular measurements from standard fundus images, and estimated fluidynamic parameters using a simple haemodynamic model. We show that there are statistically significant changes in some estimated haemodynamic parameters associated with the development of DR.